“Adult polycystic liver disease (PCLD) is an autosomal dominant condition commonly associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). However
in the last decade, it has been recognized that there is a distinct form of autosomal dominant PCLD that arises without concomitant ADPKD. Early knowledge of the pathogenesis was gained from the study of hepatic cysts in patients with ADPKD.”
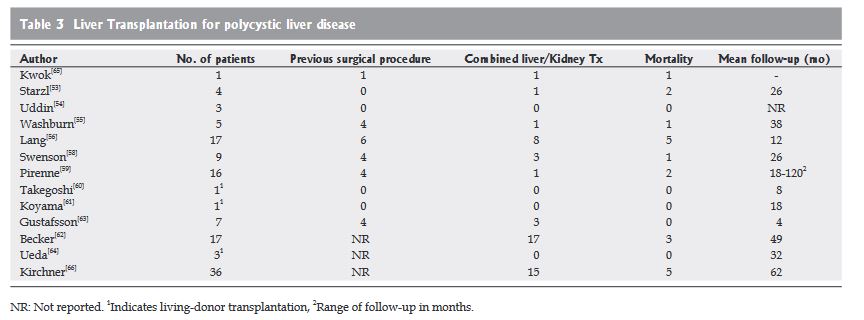
Liver transplantation as treatment for advanced PCLD, while more accepted in recent literature, still has a limited role in management of these patients. Although a majority of PCLD patients have normal liver function, orthotopic and living donor liver transplantation have been successfully utilized in the treatment of symptomatic PCLD[53-64]. Aspiration, fenestration, or surgical resection can provide adequate palliation to those patients with large single cysts or dominant disease in one lobe, but the treatment of small, truly diffuse, cystic type PCLD
may well require transplantation. Total hepatectomy and liver transplantation offers the chance of definitive treatment for this disease, but may be considered drastic, considering the absence of liver failure, the potential morbidity and mortality, and the organ shortage.”
Russell RT, Pinson CW. Surgical management of polycystic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Oct 14;13(38):5052-9.
