“Distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy (DPS) is performed to remove pathology of the body and/or tail of the pancreas. The spleen and the left side of the pancreas share blood supply, and often tumor involvement, thus splenectomy is often performed along with distal
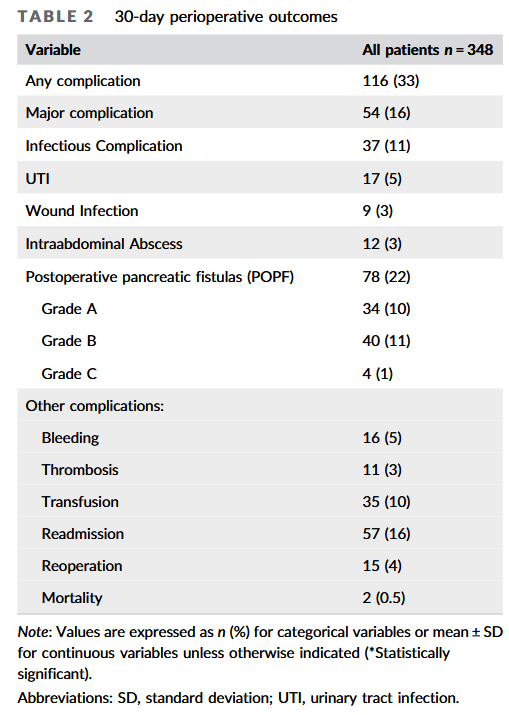
pancreatectomy. DPS is an operation that carries a greater than 30% risk of postoperative complications, including infection, postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF), intraabdominal abscesses, and pneumonia, among others. In addition to these immediate postoperative
complications, splenectomy itself is known to confer long‐term susceptibility to infection, sepsis, thrombosis, and other sequelae. Our goal was to identify factors that could prompt early investigation and treatment of both infectious and major complications.”
“Postsplenectomy diagnosis of complications based on WBC elevation is confounded by an expected, physiologic leukocytosis. The findings of our large, thorough analysis of these indices in DPS were consistent with those in other literature for splenectomy alone.
Differences exist in WBC counts and PC/WBC ratios that correspond statistically with the likelihood of developing infections or major complications; however, the differences are subtle and no clear discriminating cutoffs or patterns were identified. Patterns of WBC
correlated with other factors such as temperature and PC/WBC ratio may have more potential as a predictive model and may be further explored. Clinical suspicion remains the most important tool in identifying complications status post distal pancreatectomy with
splenectomy.”
Labib, Jessica Y et al. “Implications of leukocytosis following distal pancreatectomy splenectomy (DPS) and association with postoperative complications.” Journal of surgical oncology vol. 126,6 (2022): 1012-1020. Full Text for Emory Users
