“Operative internal drainage has been standard treatment for chronic unresolved pancreatic pseudocysts (PPs). Recently, percutaneous external drainage (PED) has become the primary mode of treatment at many medical centers.”
“ Operative management for PPs appears to be superior to CT-guided PED. Although the later was often successful, it required major salvage procedures in one third of the patients. An expectant management protocol may be suitable for selected patients.”
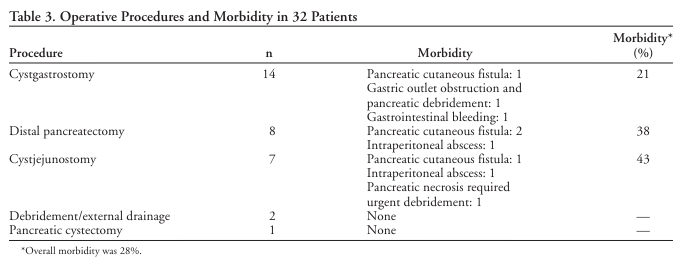
“There are numerous surgical options for the treatment of PP. The primary consideration is the anatomic location of the cyst followed by its size and the degree of chronic pancreatic disease. Cysts that are located at the tail of the pancreas may be managed by distal pancreatectomy if the remaining pancreas is sufficient (about one third of original size) for endocrine or exocrine function. On rare occasions, a simple cystectomy may also be an option. PPs that are more centrally located are best drained internally.”
“Historically, internal drainage has been the mainstay of treatment for PP. With the improvement of technology and increasing experience, however, PP drainage is often carried out percutaneously under sonographic or CT guidance. CT-guided PED appears to be a very attractive option. It is performed in the radiology suite and is considered “minimally invasive,” avoiding a relatively major operation. The principle drawback, however, of this technique is that it substitutes external drainage through a small catheter for wide internal drainage. These catheters are prone to clogging with pancreatic debris, resulting in failure of drainage and infection secondary to introduction of contaminating organisms”
Spivak, H et al. “Management of pancreatic pseudocysts.” Journal of the American College of Surgeons vol. 186,5 (1998): 507-11. Full Text at Emory.
