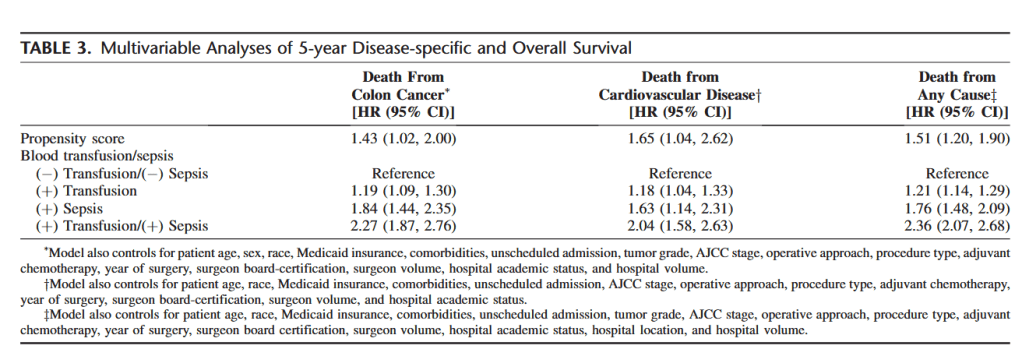
“Colorectal cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer-related mortality in both the United States and Europe. With respect to prognosis, increasing evidence has suggested that systemic inflammation is a key predictor of disease progression and survival for colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgery. Furthermore, whereas red blood cell (RBC) transfusions may be life-saving in some circumstances, there has been growing evidence that transfusions are associated with adverse postoperative outcomes, including infectious complications and cancer recurrence. These detrimental effects are thought to be related to systemic inflammation and transfusion-related immunomodulation (TRIM). Whereas the exact mechanisms remain unknown, TRIM seems to be related to various immunologic changes, including decreased interleukin (IL)-2 production, monocyte and cytotoxic cell activity inhibition, increased suppressor T-cell activity, and immunosuppressive prostaglandin release.”