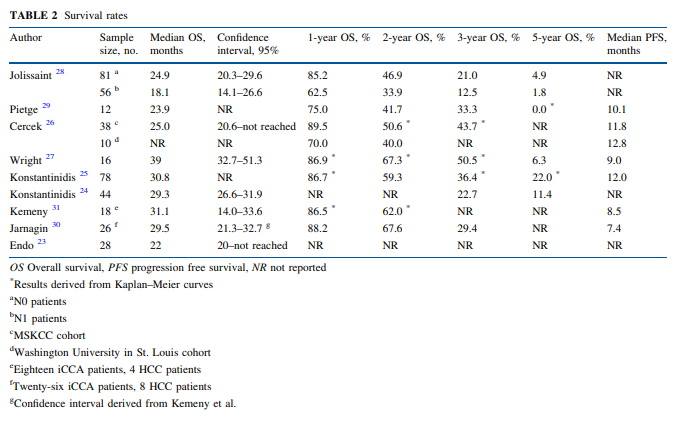
“Because most patients die from progressive disease in the liver, hepatic arterial infusion pump (HAIP) chemotherapy with floxuridine is an attractive treatment option for unresectable [Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma] iCCA. The rationale for HAIP chemotherapy is that iCCA relies mostly on arterial blood supply. Moreover, floxuridine, also known as FUDR, is characterized by its high first-pass effect; approximately 95% is directly metabolized in the liver. Hence, this allows for an up to 400-fold dose increase in subsequent intratumoral exposure compared with systemic treatment, with minimal systemic exposure and side effects”