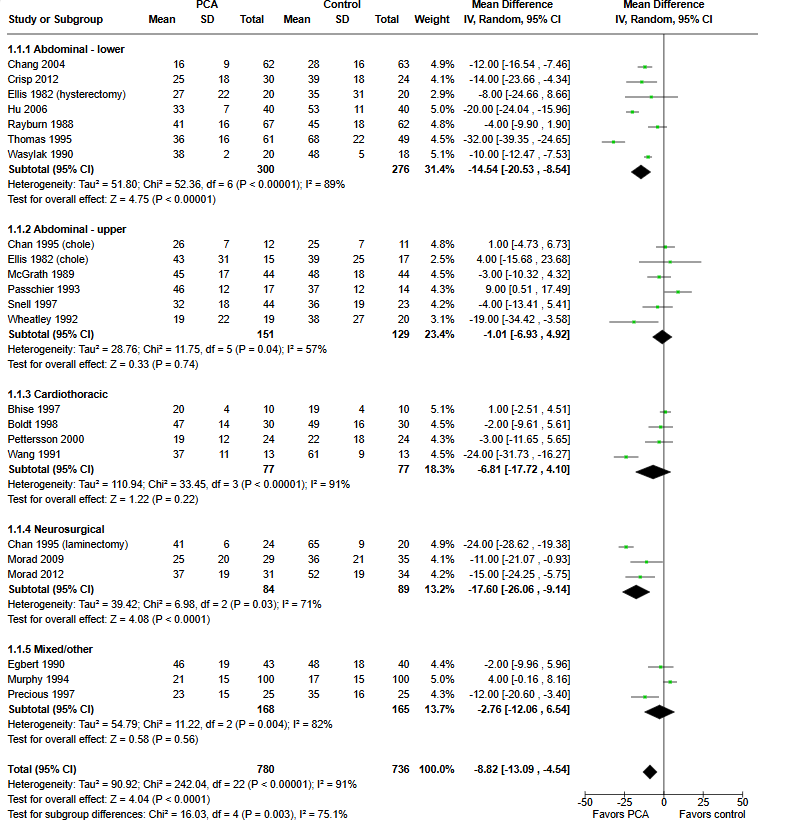
“Patients may control pain after surgery by self administration of analgesics (pain killers) using devices designed for this purpose (patient controlled analgesia or PCA). PCA involves self administration (by pushing a button) of small doses of opioids (such as morphine)
intravenously by means of a programmable pump. Previous studies have shown that often patients prefer PCA to traditional methods of pain management, such as a nurse administering an analgesic upon a patient’s request. This review demonstrated moderate to low quality evidence that PCA provided slightly better pain control and increased patient satisfaction when compared with non-patient controlled methods. Patients tended to use slightly higher doses of medication with PCA and suffered a higher occurrence of itching, but otherwise side effects were similar between groups.”