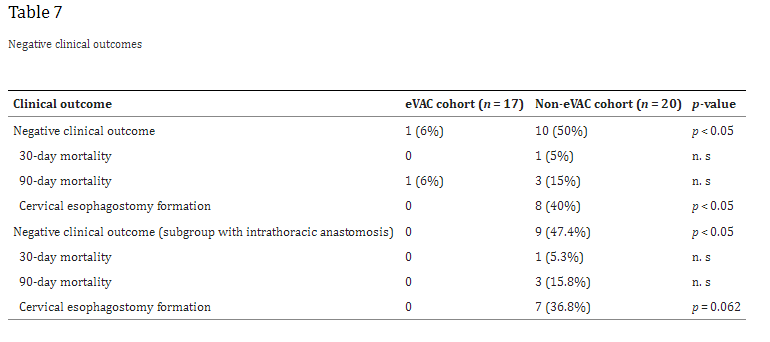
“Anastomotic leakages continue to be a highly challenging complication in esophageal surgery. According to the literature, the risk of anastomotic leakage after esophagectomy ranges between 4 and 35%. The location of the anastomotic leakage is a significant factor in determining patient outcomes. Notwithstanding, cervical anastomoses bear a higher risk for leakage; the consequences of an intrathoracic (mediastinal) leakage are usually more devastating. A leakage into the thoracic cavity typically leads to mediastinitis and severe pneumonia and contributes to the significant mortality rates in esophageal surgery. In contrast, cervical anastomotic leakages tend to frequently present as wound infections often only requiring external drainage”
“The clinical outcomes strongly depend on an early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, which can extent over several weeks or even months. In the past, the mainstay of treatment was based on surgical repair, external drainage of sepsis via chest tubes, and interventional treatment modalities like endoscopic stent deployment or clipping. In 2008, endoscopic vacuum-assisted closure (eVAC) therapy was successfully applied in patients with anastomotic leakages after esophagectomies. As in other vacuum-assisted wound therapies, eVAC cleans the defect by reducing the amount of exudative fluids and necrotic tissue, thus accelerating the healing process by contributing to a better local perfusion as well as through the formation of granulation tissue.”