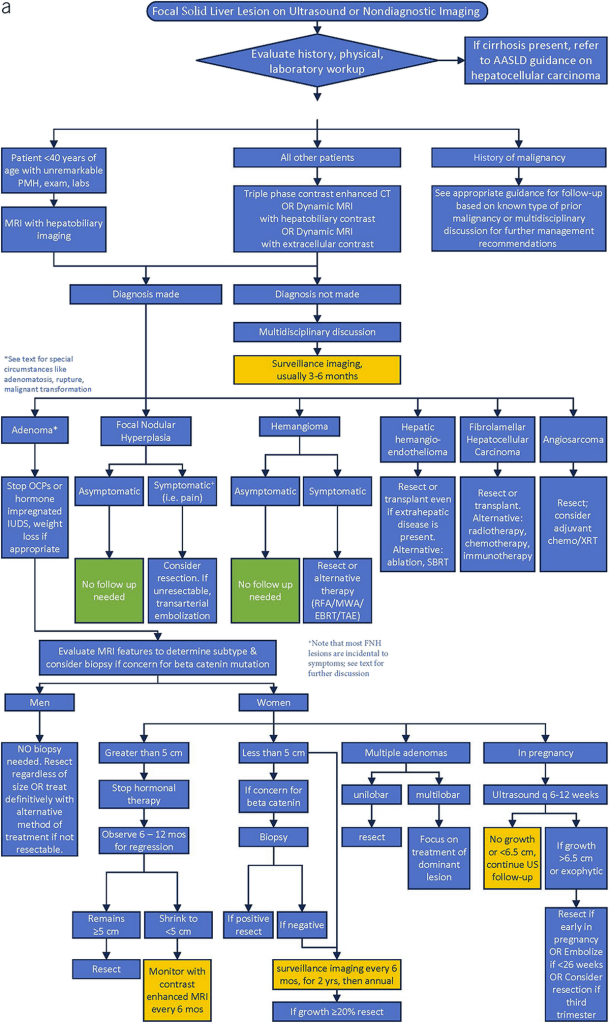
“With the continued dramatic rise in the widespread role of imaging in diagnosis and management of patients, there is a resultant rise in detection of asymptomatic incidental liver lesions. Common imaging modalities in which incidental liver lesions are detected include ultrasonography (US) with or without contrast agent (CEUS), computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for abdominal or nonabdominal indications (breast and spine). Studies show a continued upward trend in utilization of CT/MRI/US imaging in adults in the United States and Canada, inevitably resulting in increased detection of incidental FLLs within the liver. In fact, some studies show that up to 52% of patients without cancer have a benign liver lesion at autopsy. The American College of Radiology reports that up to 15% of patients have an incidental liver lesion detected
on routine nonsurveillance imaging. Therefore, it is critical to understand appropriate management of incidentally detected benign FLLs because they have differing clinical implications from malignant lesions such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA), and metastatic disease.”