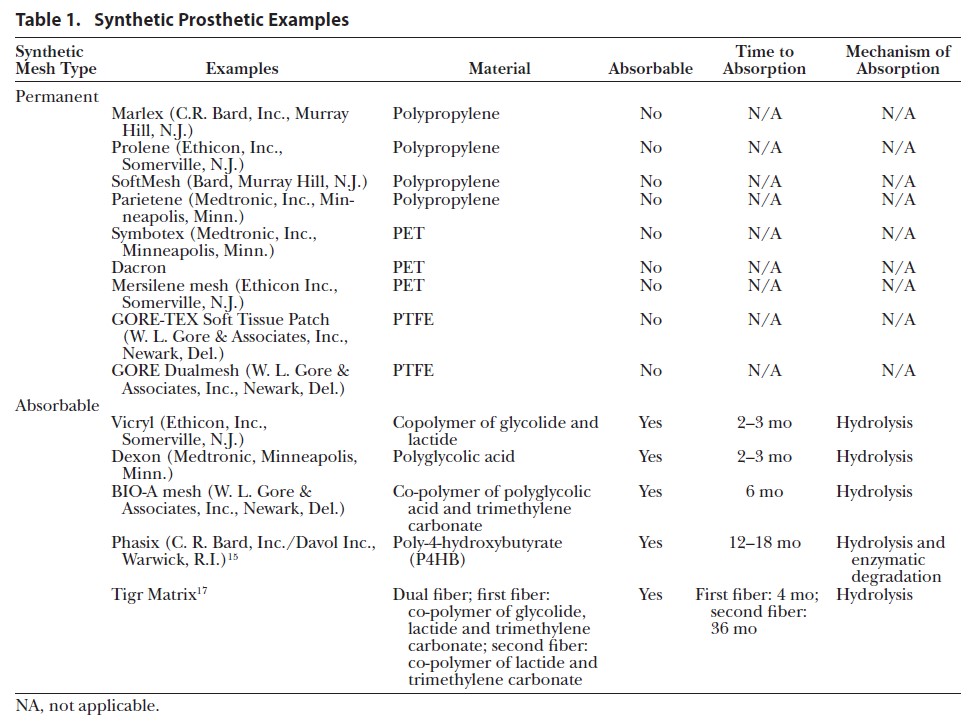
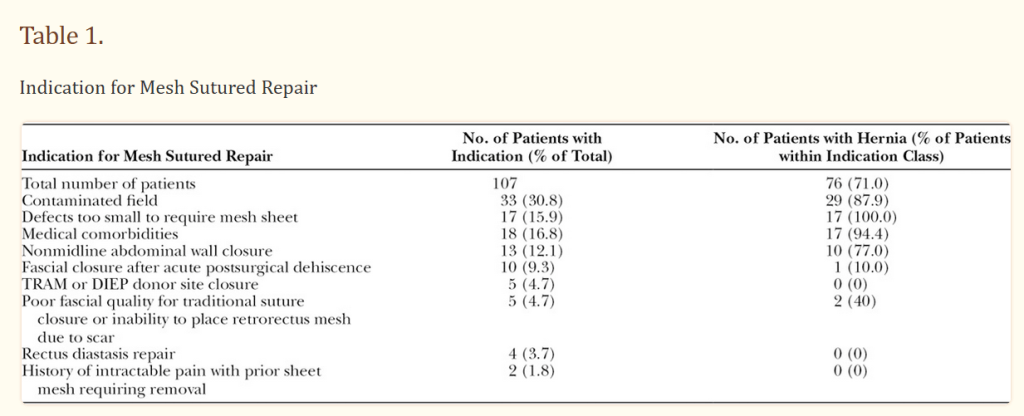
“Incisional hernias are an increasingly common complication encountered by surgeons and their patients, as survival rates from major abdominal surgery continue to improve. The
incidence of incisional hernia after midline laparotomy is estimated to be 9%–20% after 1 year, resulting in approximately 8000 UK repairs annually. While patient factors such as obesity, smoking and diabetes certainly contribute, excessive suture tension during the critical wound healing period causes local ischaemia at the suture-tissue interface and may initiate incisional hernia. Subsequent suture “cheese-wiring” through fascia creates small linear defects that enlarge over time with repeated abdominal wall straining. The clinical
and economic implications of incisional hernia have precipitated preventative research, including Jenkins rule, small-bite closure, and prophylactic mesh implantation which are
discussed in recent high-profile international guidelines. However, many surgeons continue to adopt suture closure over prophylactic planar mesh since this prolongs surgery and risks
infection in a contaminated field.”
Nip, Lawrence et al. “Mesh Suture and Mesh Strips to Prevent Incisional Hernia Following Abdominal Wall Closure or Ventral Hernia Repair: Systematic Review.” Journal of abdominal wall surgery : JAWS vol. 4 14573. 14 May. 2025 Free Full Text