“Surgical site infections after gastrointestinal perforation with peritonitis have significant
morbidity, increased hospital stays, and cost of treatment. The appropriate management of these wounds is still debatable.”
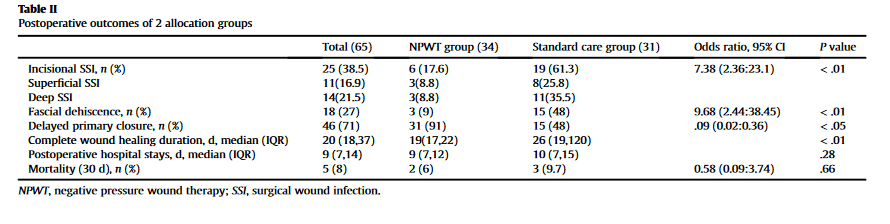
“In this single-center randomized controlled trial, we found that the use of NPWT on the surgical incision in patients with GIP significantly reduced the rate of SSI and wound dehiscence. The overall incidence of SSI in the present study was 38.5%. The use of
NPWT also significantly increased the rate of delayed primary wound closure and improved wound healing time.”