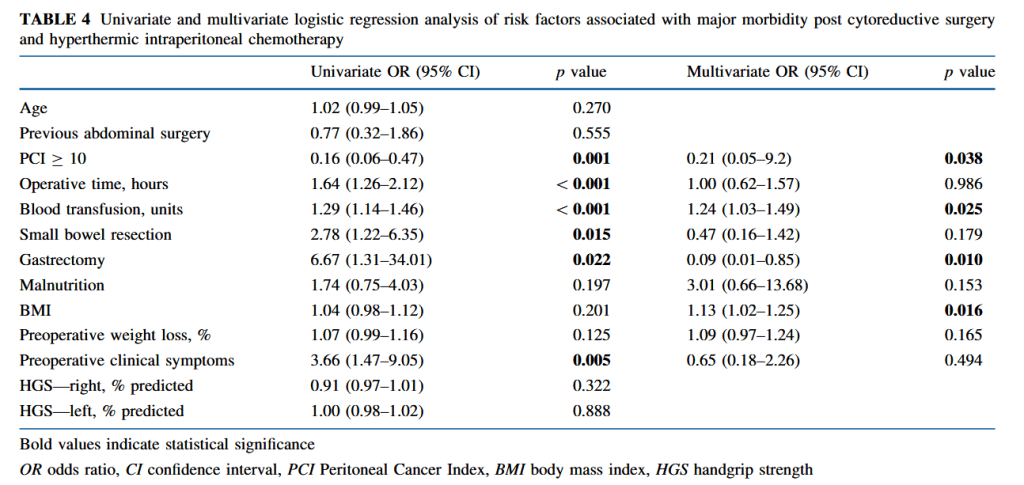
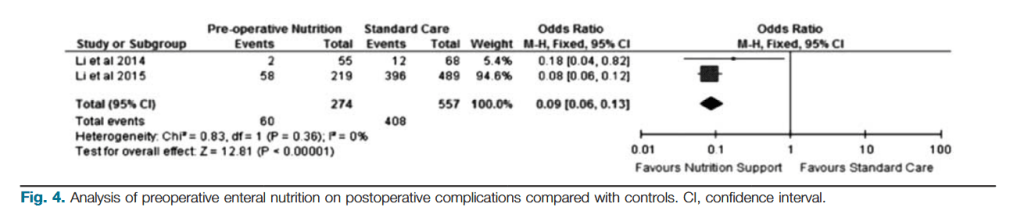
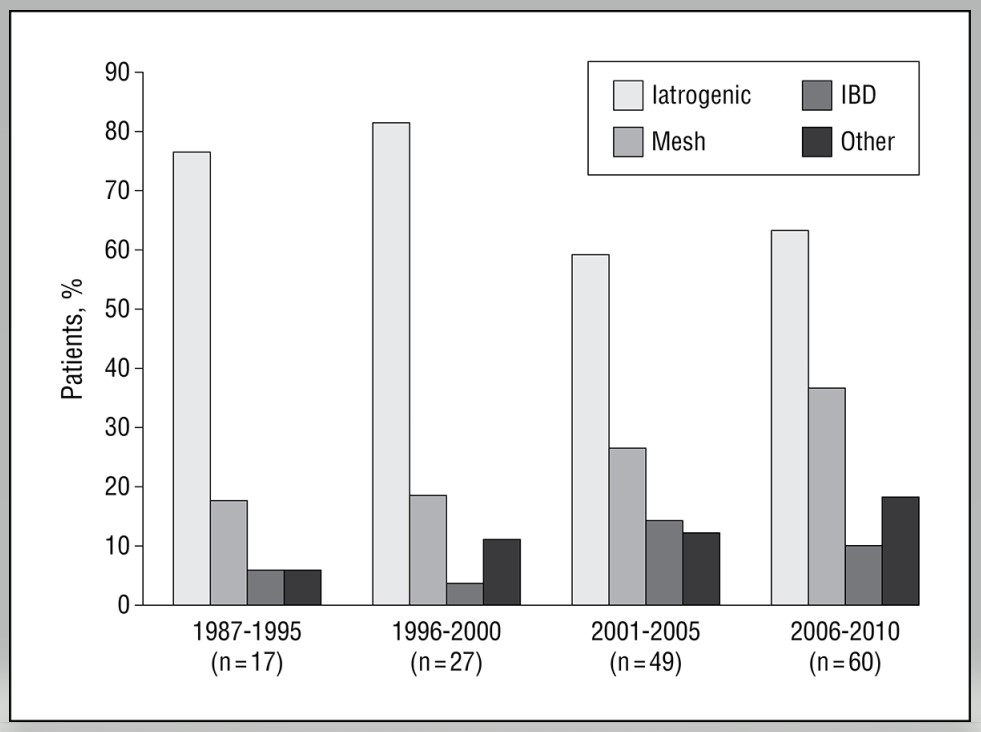
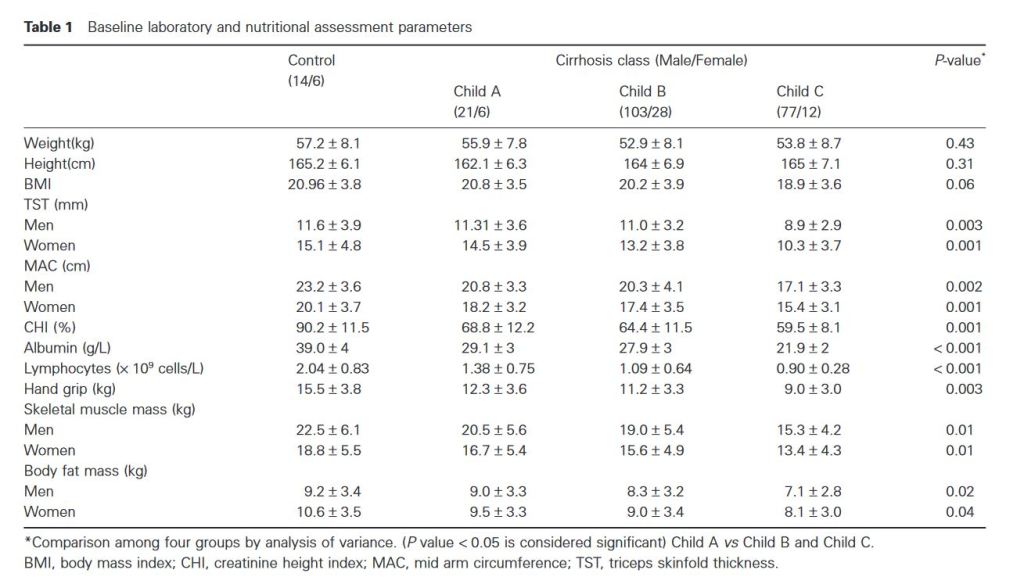
“Cytoreductive surgery (CRS) and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) is complex surgery to treat peritoneal surface malignancy (PSM). PSM arises from gastrointestinal (GI), gynecological, or primary peritoneal cancers. CRS aims to completely remove macroscopic tumor. In order to achieve complete cytoreduction, multiple abdominal organ resections are often necessary. After cytoreduction, HIPEC is delivered into the abdominal cavity for 30–90 min to treat residual microscopic disease.”
“Malnutrition is prevalent in patients undergoing surgery for abdominopelvic malignancy and is associated with increased morbidity, longer hospital length of stay (LOS), and mortality. Preoperative malnutrition is a risk factor for organ dysfunction, impaired immune function,
wound complications, impaired physical function, and increased LOS. Malnutrition prevalence is documented in up to 67% of patients with ovarian cancer and 30–50% of patients with colorectal cancer.”