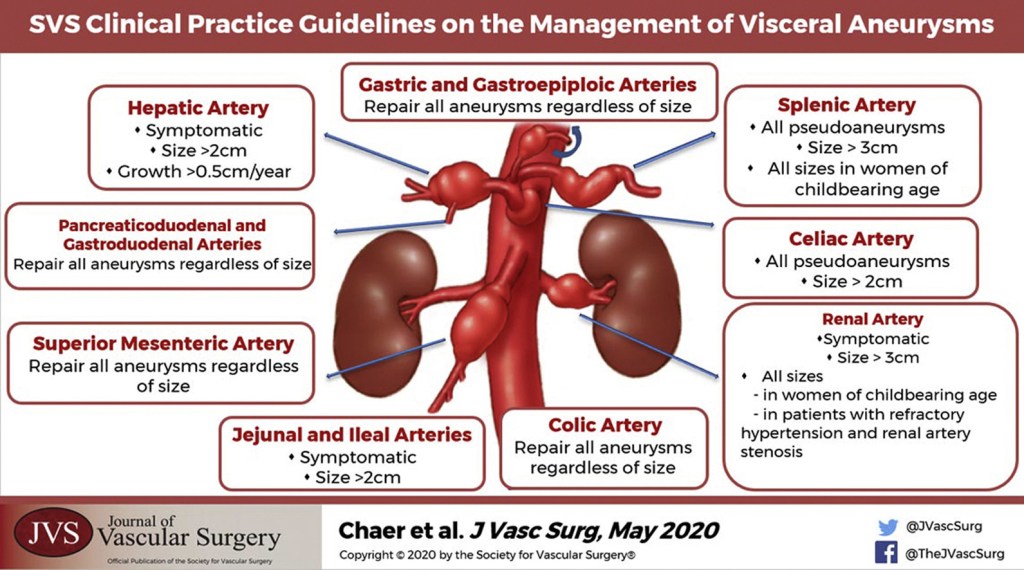
“Although not directed by randomized prospective trials, general principles of management of visceral artery aneurysms do exist. Because of their potential for rupture, most visceral artery pseudoaneurysms, mycotic aneurysms, and many larger true aneurysms warrant intervention. Treatment can generally be accomplished by either open surgical or endovascular approaches. The treatment goal is to prevent aneurysm expansion and potential rupture by exclusion from the arterial circulation while maintaining necessary distal or collateral bed perfusion. Depending on the location of the aneurysm, this can be accomplished in a variety of ways. In areas of the visceral circulation with an abundance of collateral flow, for example, in the splenic artery, proximal and distal ligation of the aneurysm segment is a viable surgical option. This can also be accomplished with endovascular isolation of the aneurysmal segment, either by placement of a stent graft or by coil embolization of the proximal and distal arterial segment. The preferred treatment of an individual patient and aneurysm must be carefully based on the particular anatomy and any associated clinical conditions as well as the underlying condition of the patient. The purpose of these guidelines is to inform the diagnosis, treatment options, screening, and follow-up of visceral aneurysms based on the available published literature and the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) approach”