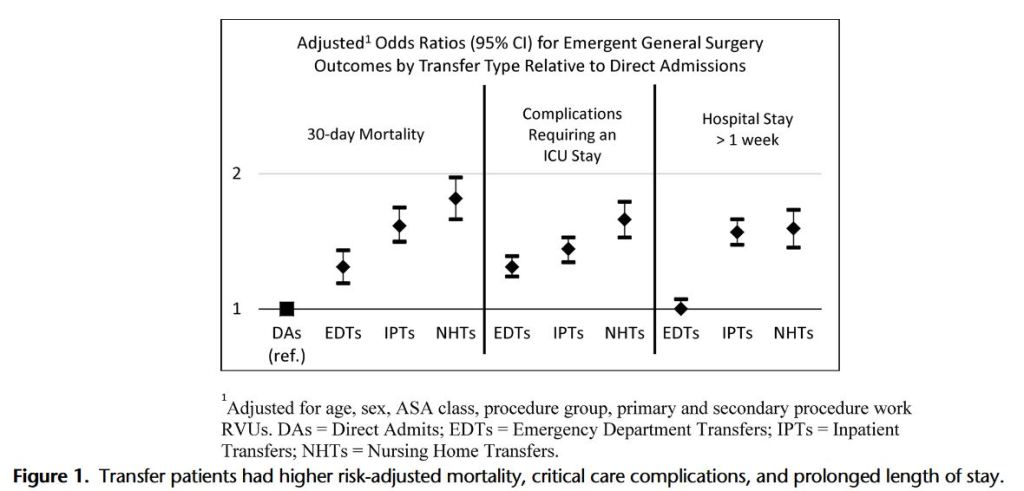
“Emergency general surgery (EGS) patients require greater resources and have increased rates of morbidity and mortality. Previous work has shown mortality differences in colectomy patients between direct admissions and transfers patients based on source, including emergency department, inpatient, and nursing home transfers. We hypothesize that patient transfer status negatively effects morbidity, mortality, and resource utilization in a mixed population of EGS patients.
This study demonstrates significant increases in mortality, morbidity, and resource utilization in EGS transfer patients who were not attributable to case mix, demographics, and comorbid status alone. These data point to potential financial and quality assessment challenges for tertiary referral centers.”