“The number of people over 65 years is increasing and will continue to do so over the coming decades. Similarly, the number of elderly patients requiring surgery is expected to increase.
Delirium is a common and serious problem in hospitalized patients, especially in the elderly.
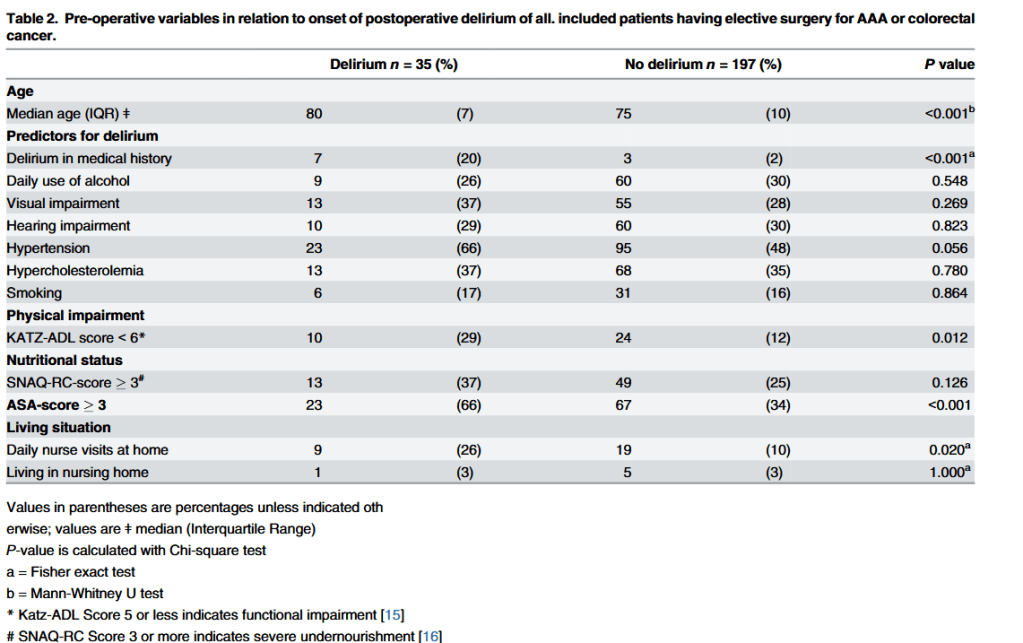
Postoperative delirium is associated with an increase in postoperative complications, a decrease in functional capacity, a prolonged hospital stay and a direct increase of healthcare costs.
Early identification of patients at risk for delirium is important because adequate well timed
interventions could prevent occurrence of delirium and the related detrimental outcome.
Several prediction models have been developed, including multiple risk factors for postoperative delirium. However, these studies are of varying quality and each with a heterogeneous population.
Measuring frailty may be a more sensitive marker of determining post-operative delirium. However, to this date, there is no consensus on a clear definition and quantification of
frailty. Several assessment instruments have been developed for frailty during the last decades.
The most evidence based process to identify frail patients at this moment is comprehensive
geriatric assessment. However, this is a resource intensive, time consuming process and therefore not suitable for clinical practice”