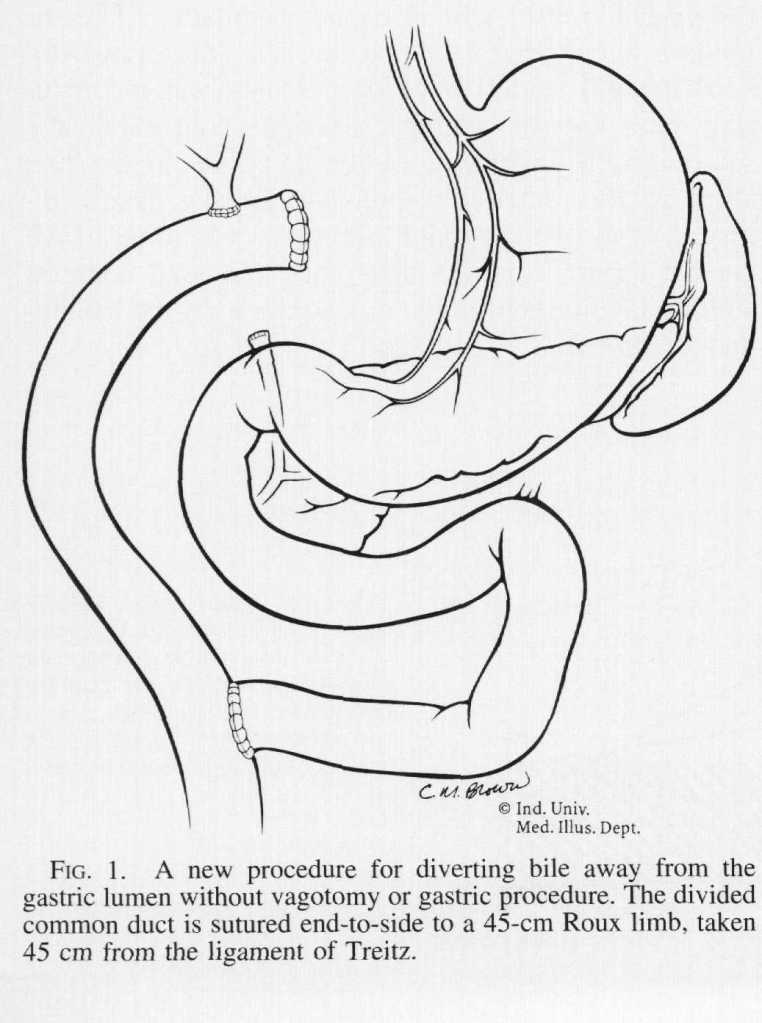
“Various treatments for [Primary Bile Reflux Gastritis] have been proposed since its recognition. Operations that have been utilized are the Roux-en-Y procedure, the Braun enteroenterostomy, the Henley jejunal interposition, and several modifications of each of these operations. These procedures produce relief from bile reflux, but all have particular side effects of their own. Before the utilization of vagotomy for ulcer disease, stomal ulceration at the gastrojejunal anastomosis was the most frequent postoperative problem. Currently, the most commonly applied operation is the Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy, which requires vagotomy and antrectomy and results in the equally disabling Roux stasis syndrome in about one-half of patients.”
“Because of these difficulties, a new procedure is proposed wherein only bile is diverted by means of a Roux-en-Y limb and no gastric procedure is done. This allows minimal disturbance of gastric motility and totally diverts bile away from the gastric lumen.”