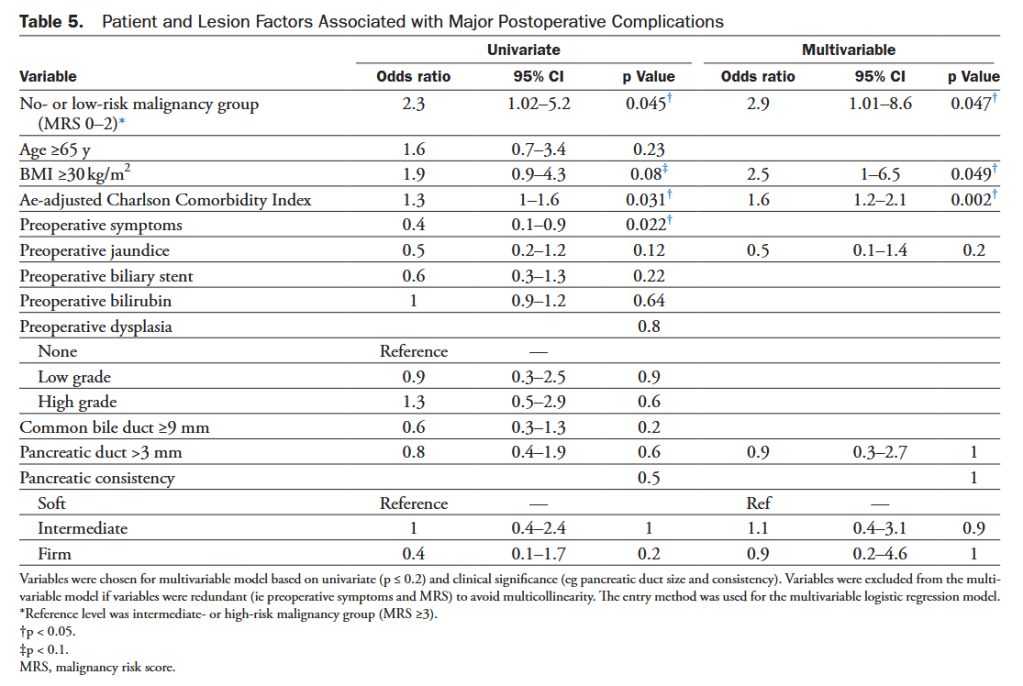
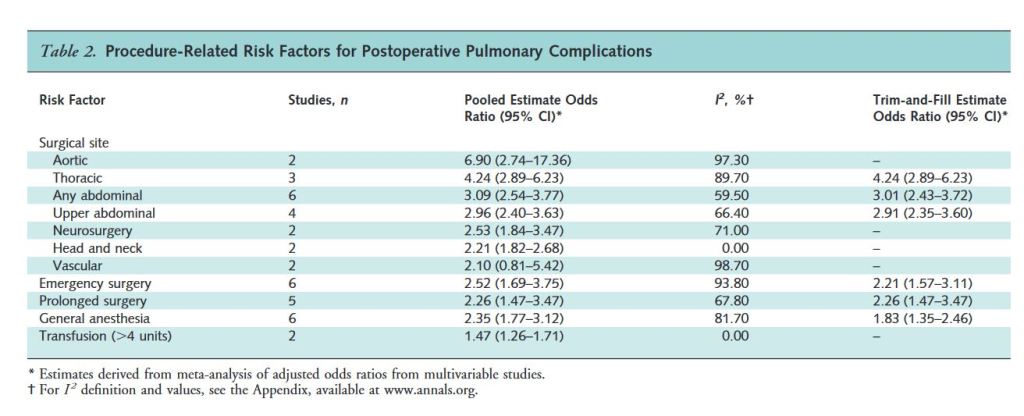
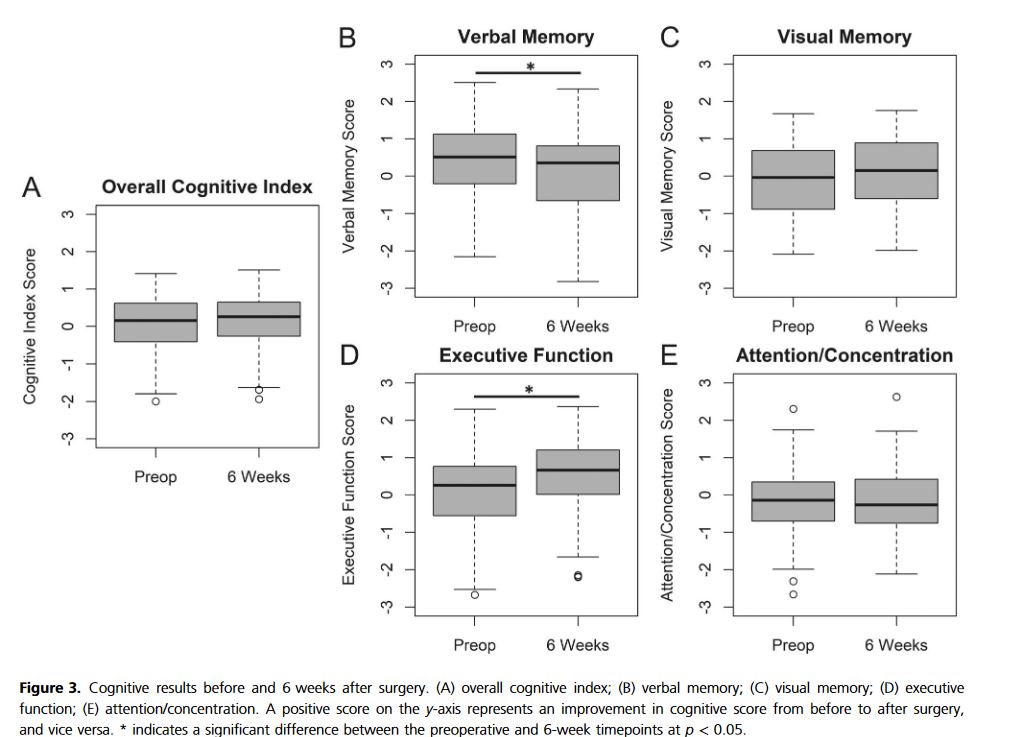
“Preoperative assessment of underlying malignancy in non-FAP-related PAs requiring PD may be difficult, as endoscopic biopsy carries a false-negative rate as high as 50%. Although PD aims at preempting malignant transformation through complete removal of DA, it comes with significant morbidity and mortality risks. This is particularly relevant in patients with benign or premalignant pathology due to soft pancreatic parenchymal texture and small pancreatic duct diameter.”