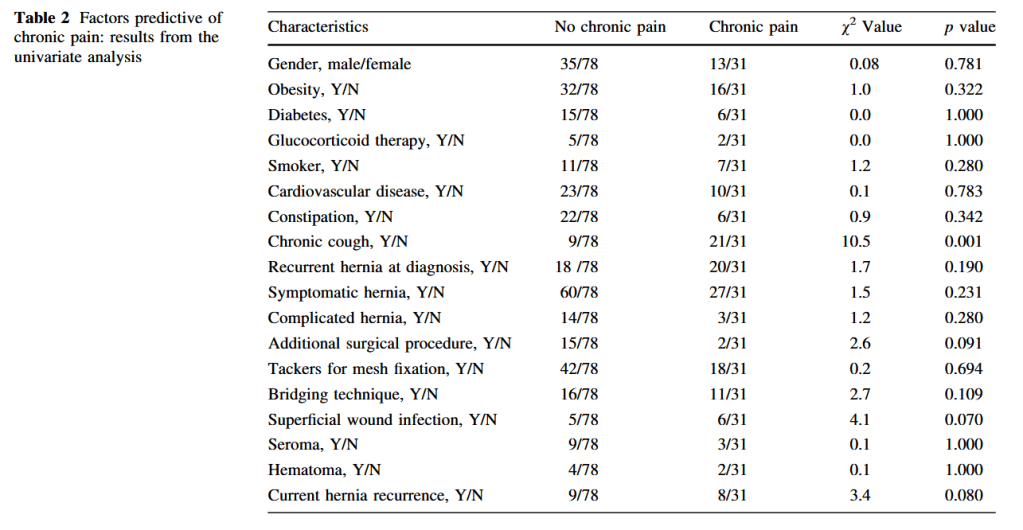
“Incisional hernia is one of the most frequent long-term complications after abdominal surgery (11%–20%). After primary repair, rates of recurrence range from 24% to 54%. It has been clearly demonstrated that the use of prostheses for a tension-free repair allows for a
significant reduction in recurrence rate, and even for the treatment of small defects. However, the type and position of the mesh and the mesh fixation technique used are still a matter of debate. The underlay position of the mesh allows for easy treatment of major parietal defects with limited dissection and potentially lower rates of mesh infection, but this position exposes the patient to the risk of small bowel occlusion and enterocutaneous fistula.”