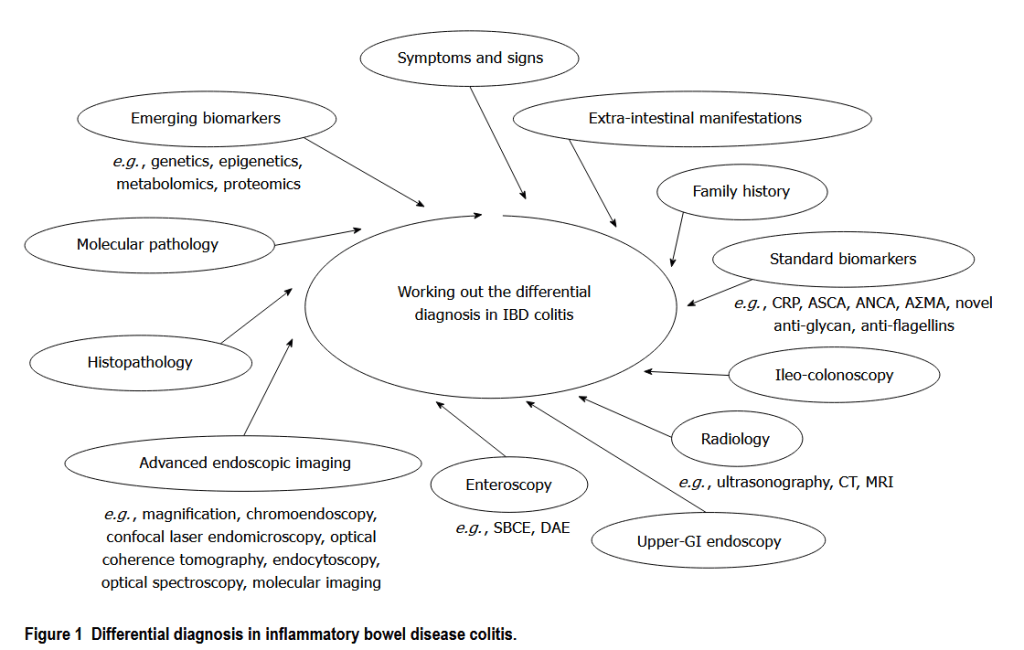
“Distinction between Crohn’s disease of the colon-rectum and ulcerative colitis or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) type unclassified can be of pivotal importance for a tailored clinical management, as each entity often involves specific therapeutic strategies and prognosis. Nonetheless, no gold standard is available and the uncertainty of diagnosis may frequently lead to misclassification or repeated examinations. Hence, we have performed a literature search to address the problem of differential diagnosis in IBD colitis, revised current and emerging diagnostic tools and refined disease classification strategies. Nowadays, the differential diagnosis is an untangled issue, and the proper diagnosis
cannot be reached in up to 10% of patients presenting with IBD colitis.”