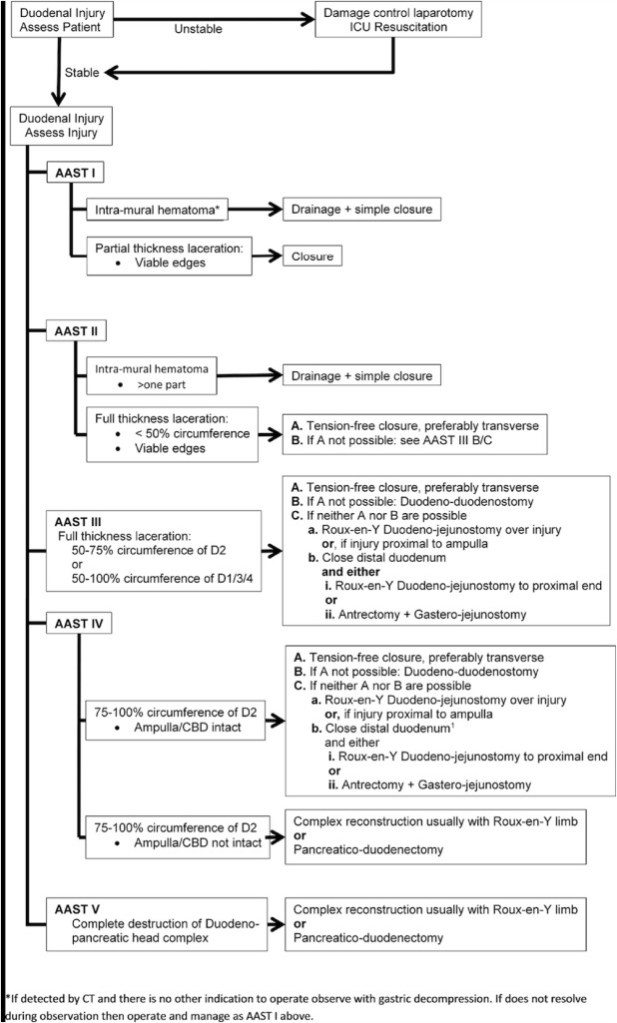
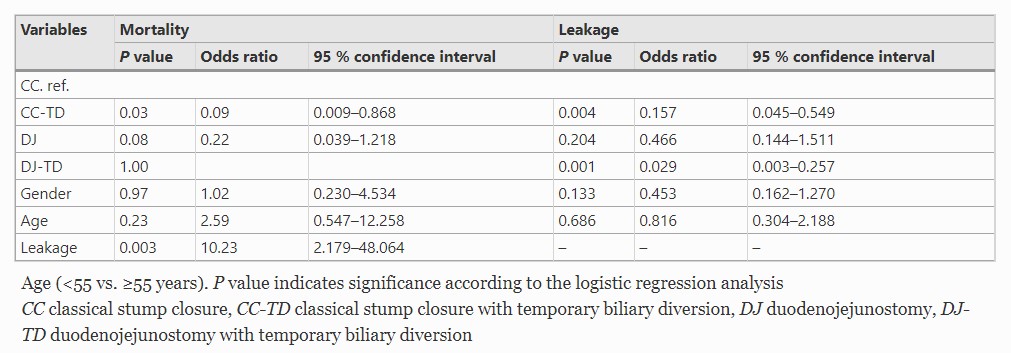
“Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy, although technically demanding, eliminates the need for pancreatic resection. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy is associated with good absorptive capacity, weight gain, and quality of life. Furthermore, it may reduce the risk of subsequent malignancy. Long-term surveillance, however, is still required. Pancreas-sparing duodenectomy is contraindicated in the setting of malignancy.”