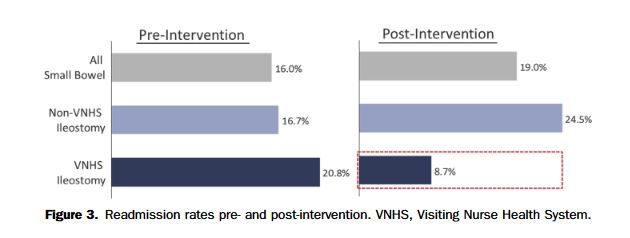
“Nearly 30% of patients with newly formed ileostomies require hospital readmission from severe dehydration or associated complications. This contributes to significant morbidity and rising healthcare costs associated with this procedure. The aim of this study was to design and pilot a novel program to decrease readmissions in this patient population.”
“Implementation of a novel program reduced the 30-day readmission rate by 58% and cost of readmissions per patient by >80% in a high risk for readmission patient population with newly created ileostomies. Future efforts will expand this program to a greater number of patients, both institutionally and systemically, to reduce the readmission-rate and healthcare
costs for this high-risk patient population.”