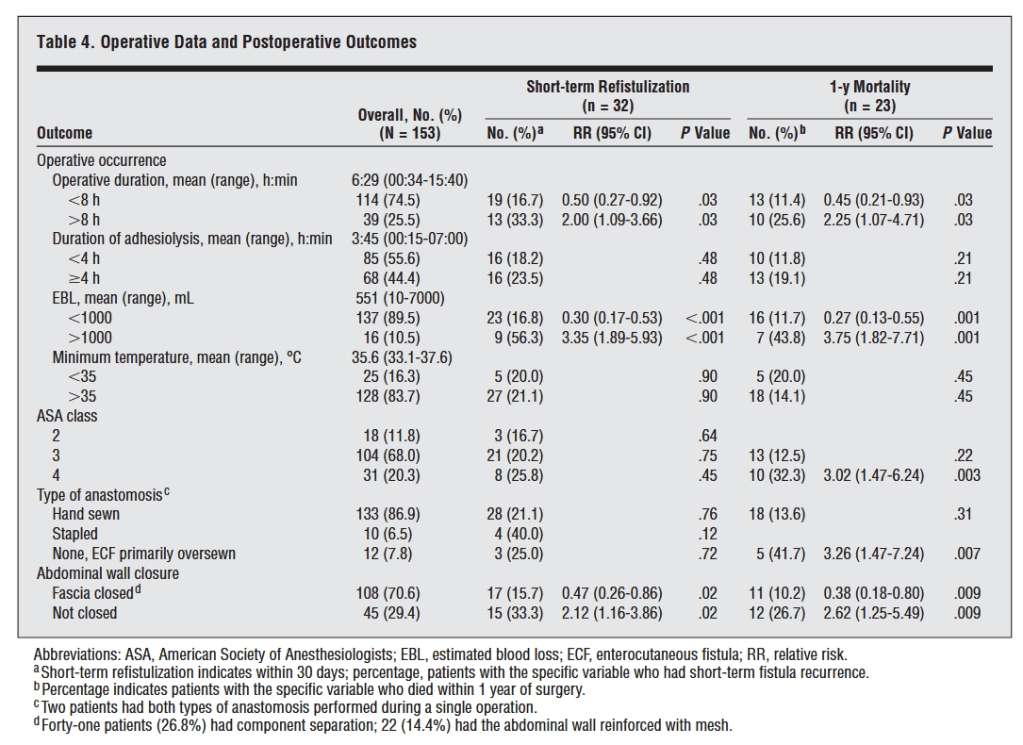
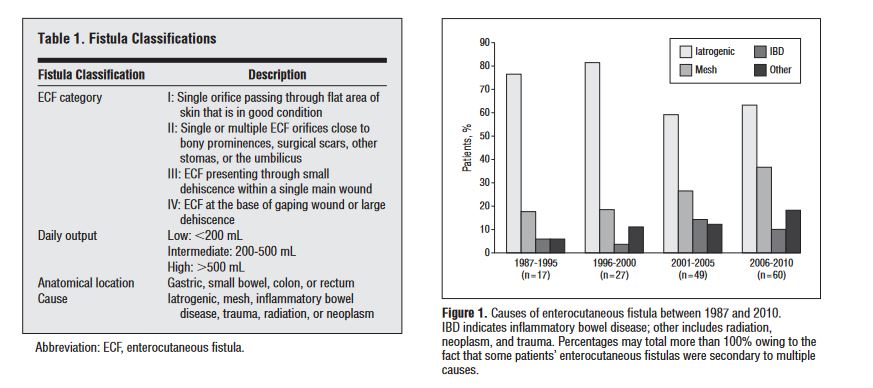
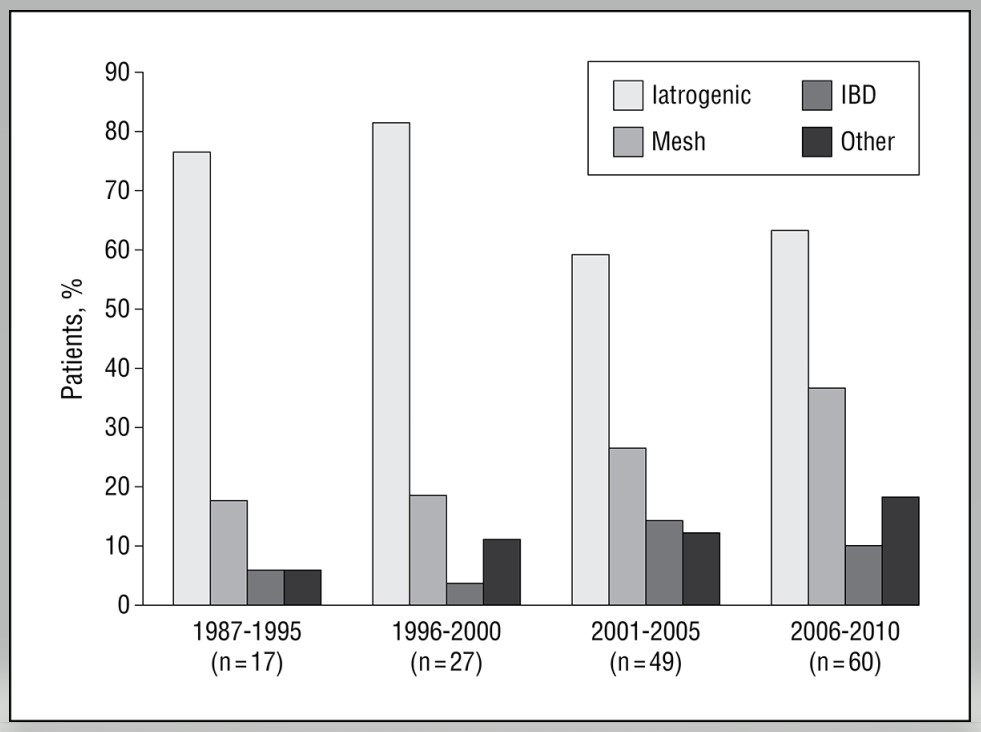
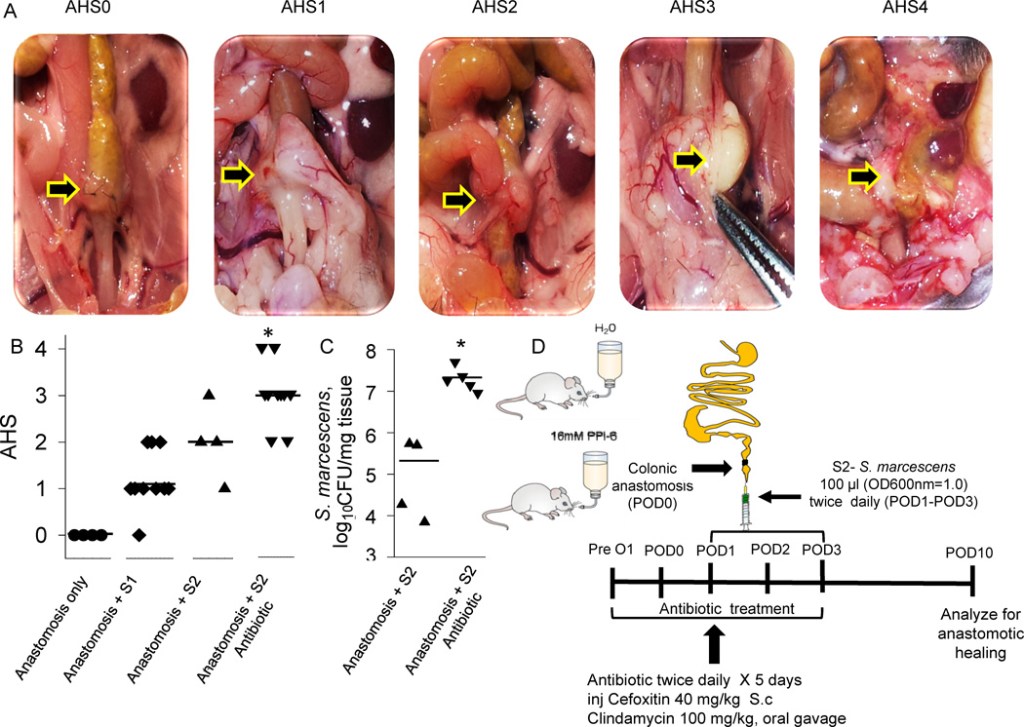
“Hartmann’s procedure involves segmental colonic resection with end-colostomy or end-
ileostomy and closure of the distal colonic/rectal remnant (DCRR), which remains in the
pelvis or abdomen as a blind-ending pouch (Hartmann’s pouch). This procedure is
commonly performed in emergency situations in patients who require partial colectomy and
are deemed to be at high risk of complications from a primary bowel anastomosis. The number of patients who undergo takedown of their stoma as a second-stage procedure varies between 56% and 100%.
Preoperative DCRR evaluation by means of contrast and/or endoscopic studies is routinely
requested by many surgeons to exclude leak, stricture, inflammation, and tumors, which
could preclude Hartmann’s reversal. DCRR evaluation is safe and has only minor
disadvantages including cost, radiation exposure, and patient discomfort. However, there is
no clear evidence that this practice affects surgical management or benefits patients. A
previous study reported abnormalities in 16% of routine contrast DCRR studies, although
these altered treatment in only a small minority of cases. In addition, the role of endoscopy
in this setting has not been defined.”
“Between 1993 and 2008, 203 patients underwent reversal of Hartmann’s at a tertiary
referral center. Sixty-eight patients (33%) did not undergo preoperative DCRR evaluation and had comparable demographic characteristics, comorbidities, DCRR length, and perioperative outcomes to 135 patients who underwent preoperative contrast and/or endoscopic studies. After evaluation, 125 (93%) patients had normal findings, seven (5%) patients had abnormal studies that did not impact their management, and three (2%) patients underwent additional procedures.”