De Laet IE, et al. A Clinician’s Guide to Management of Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients. Crit Care. 2020 Mar 24;24(1):97.
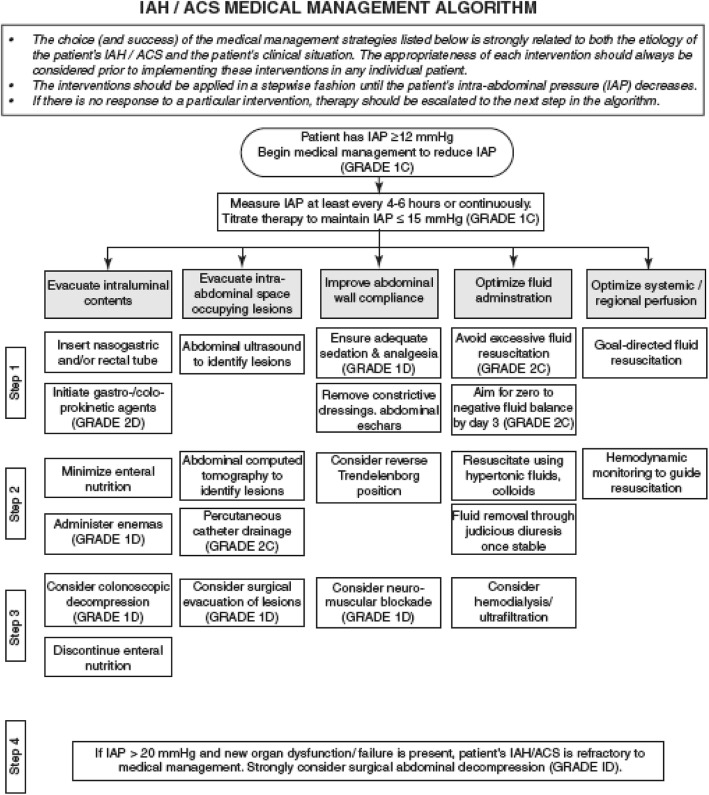

De Laet IE, et al. A Clinician’s Guide to Management of Intra-abdominal Hypertension and Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in Critically Ill Patients. Crit Care. 2020 Mar 24;24(1):97.

Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jul 2;373(1):23-34. Erratum in: N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 29;379(22):2185. Free full-text.
Results: The median progression-free survival was 11.5 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.9 to 16.7) with nivolumab plus ipilimumab, as compared with 2.9 months (95% CI, 2.8 to 3.4) with ipilimumab (hazard ratio for death or disease progression, 0.42; 99.5% CI, 0.31 to 0.57; P<0.001), and 6.9 months (95% CI, 4.3 to 9.5) with nivolumab (hazard ratio for the comparison with ipilimumab, 0.57; 99.5% CI, 0.43 to 0.76; P<0.001). In patients with tumors positive for the PD-1 ligand (PD-L1), the median progression-free survival was 14.0 months in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group and in the nivolumab group, but in patients with PD-L1-negative tumors, progression-free survival was longer with the combination therapy than with nivolumab alone (11.2 months [95% CI, 8.0 to not reached] vs. 5.3 months [95% CI, 2.8 to 7.1]). Treatment-related adverse events of grade 3 or 4 occurred in 16.3% of the patients in the nivolumab group, 55.0% of those in the nivolumab-plus-ipilimumab group, and 27.3% of those in the ipilimumab group.
Continue readingKhan BA, et al. The Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU-7 Delirium Severity
Scale: A Novel Delirium Severity Instrument for Use in the ICU. Crit Care Med. 2017 May;45(5):851-857.

Measurements and Main Results: Patients received the CAM-ICU, Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale (RASS), and Delirium Rating Scale-Revised (DRS-R)-98 assessments. A 7-point scale (0-7) was derived from responses to the CAM-ICU and RASS items. CAM-ICU-7 showed high internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha=0.85) and good correlation with DRS-R-98 scores (correlation coefficient=0.64). Known-groups validity was supported by the separation of mechanically ventilated and non-ventilated assessments. Median CAM-ICU-7 scores demonstrated good predictive validity with higher odds (OR=1.47; 95% CI=1.30-1.66) of inhospital mortality, and lower odds (OR=0.8; 95% CI=0.72-0.9) of being discharged home after adjusting for age, race, gender, severity of illness, and chronic comorbidities. Higher CAM-ICU-7 scores were also associated with increased length of ICU stay (p=0.001).
Continue readingCleary RK, Silviera M, Reidy TJ, et al. Intracorporeal and extracorporeal anastomosis for robotic-assisted and laparoscopic right colectomy: short-term outcomes of a multi-center prospective trial. Surg Endosc. 2021 Nov 1. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08780-9.
Full-text for Emory users.
Results: There were 280 patients: 156 in the robotic assisted and laparoscopic intracorporeal anastomosis (IA) group and 124 in the robotic assisted and laparoscopic extracorporeal anastomosis (EA) group. The EA group was older (mean age 67 vs. 65 years, p = 0.05) and had fewer white (81% vs. 90%, p = 0.05) and Hispanic (2% vs. 12%, p = 0.003) patients. The EA group had more patients with comorbidities (82% vs. 72%, p = 0.04) while there was no significant difference in individual comorbidities between groups. IA was associated with fewer conversions to open and hand-assisted laparoscopic approaches (p = 0.007), shorter extraction site incision length (4.9 vs. 6.2 cm; p ≤ 0.0001), and longer operative time (156.9 vs. 118.2 min). Postoperatively, patients with IA had shorter time to first flatus, (1.5 vs. 1.8 days; p ≤ 0.0001), time to first bowel movement (1.6 vs. 2.0 days; p = 0.0005), time to resume soft/regular diet (29.0 vs. 37.5 h; p = 0.0014), and shorter length of hospital stay (median, 3 vs. 4 days; p ≤ 0.0001). Postoperative complication rates were comparable between groups.
Continue readingGalyfos G, et al. Acute limb ischemia among patients with COVID-19 infection. J Vasc Surg. 2022 Jan;75(1):326-342. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2021.07.222. Epub 2021 Aug 12.
Results: In total, 34 studies (19 case reports and 15 case series/cohort studies) including a total of 540 patients (199 patients were eligible for analysis) were evaluated. All studies were published in 2020. Mean age of patients was 61.6 years (range, 39-84 years; data from 32 studies) and 78.4% of patients were of male gender (data from 32 studies). There was a low incidence of comorbidities: arterial hypertension, 49% (29 studies); diabetes mellitus, 29.6% (29 studies); dyslipidemia, 20.5% (27 studies); chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, 8.5% (26 studies); coronary disease, 8.3% (26 studies); and chronic renal disease, 7.6% (28 studies). Medical treatment was selected as first-line treatment for 41.8% of cases. Pooled mortality rate among 34 studies reached 31.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 25.4%%-37.7%). Pooled amputation rate among 34 studies reached 23.2% (95% CI, 17.3%-29.7%). Pooled clinical improvement rate among 28 studies reached 66.6% (95% CI, 55.4%%-76.9%). Pooled reoperation rate among 29 studies reached 10.5% (95% CI, 5.7%%-16.7%). Medical treatment was associated with a higher death risk compared with any intervention (odds ratio, 4.04; 95% CI, 1.075-15.197; P = .045) although amputation risk was not different between the two strategies (odds ratio, 0.977; 95% CI, 0.070-13.600; P = .986) (data from 31 studies).
Conclusions: SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with a high risk for thrombotic complications, including ALI. COVID-associated ALI presents in patients with a low incidence of comorbidities, and it is associated with a high mortality and amputation risk. Conservative treatment seems to have a higher mortality risk compared with any intervention, although amputation risk is similar.
Continue readingDeng JZ, et al. The Risk of Postoperative Complications After Major Elective Surgery in Active or Resolved COVID-19 in the United States. Ann Surg. 2022 Feb 1;275(2): 242-246.
Results: Of the 5479 patients who met study criteria, patients with peri-Covid-19 had an elevated risk of developing postoperative pneumonia [adjusted odds ratio (aOR), 6.46; 95% confidence interval (CI): 4.06-10.27], respiratory failure (aOR, 3.36; 95% CI: 2.22-5.10), pulmonary embolism (aOR, 2.73; 95% CI: 1.35-5.53), and sepsis (aOR, 3.67; 95% CI: 2.18-6.16) when compared to pre-Covid-19 patients. Early post-Covid-19 patients had an increased risk of developing postoperative pneumonia when compared to pre-Covid-19 patients (aOR, 2.44; 95% CI: 1.20-4.96). Late post-Covid-19 patients did not have an increased risk of postoperative complications when compared to pre-Covid-19 patients.
Conclusions: Major, elective surgery 0 to 4 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with an increased risk of postoperative complications. Surgery performed 4 to 8 weeks after SARS-CoV-2 infection is still associated with an increased risk of postoperative pneumonia, whereas surgery 8 weeks after Covid-19 diagnosis is not associated with increased complications.
Continue readingMirrielees JA, et al. Pancreatic Fistula and Delayed Gastric Emptying Are the Highest-Impact Complications After Whipple. J Surg Res. 2020 Jun;250:80-87.
Full-text for Emory users.
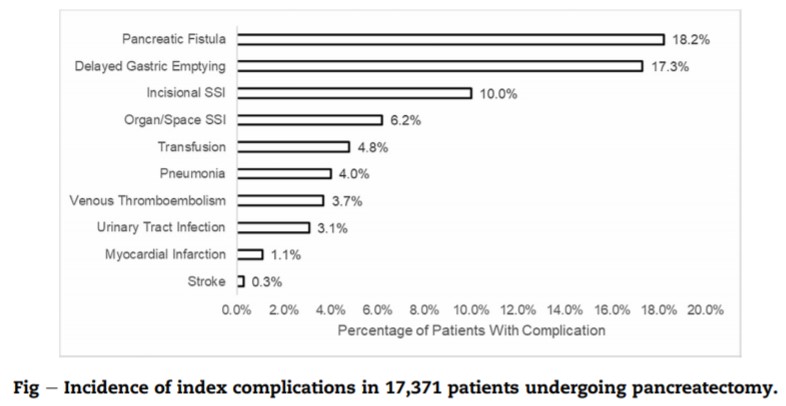
Results: About 10,922 patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy were included for analysis. The most common postoperative complications were DGE (17.3%), POPF (10.1%), incisional SSI (10.0%), and organ/space SSI (6.2%). POPF and DGE were the only complications that demonstrated sizable effects for all clinical and resource utilization outcomes studied. Other complications had sizable effects for only a few of the outcomes or had small effects for all the outcomes.
Continue reading