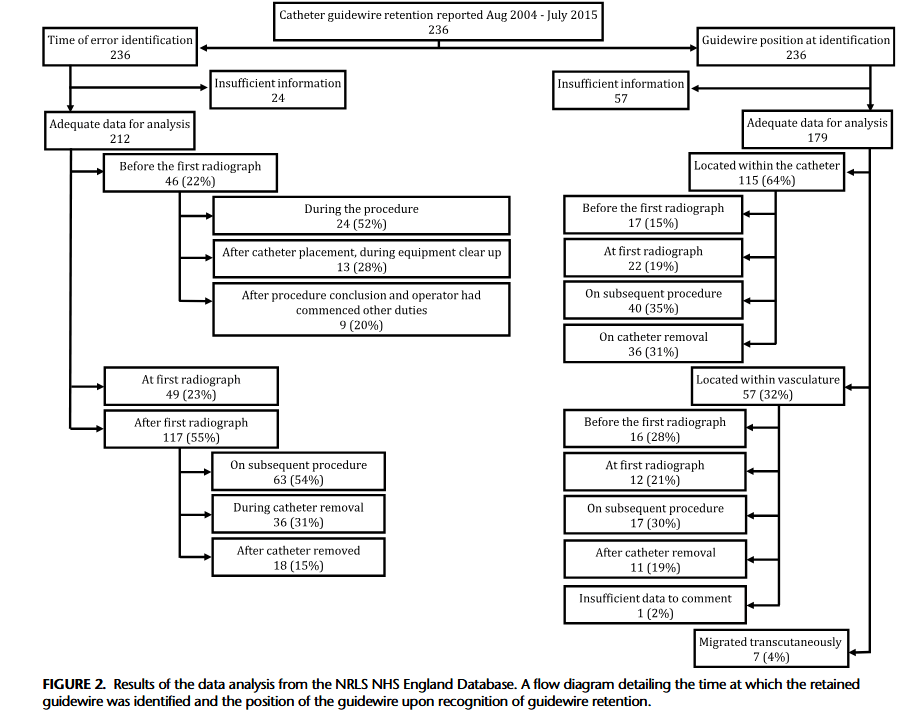
“Central venous catheters (CVC) are commonly used for monitoring and administering medication. The Seldinger technique is routinely used for CVC insertion; however, this technique has an inherent risk of guidewire retention. The mechanism behind guidewire retention is debated, with some authors reporting cases where guidewires “slip” or are sucked into the vasculature at the point of insertion, presumably due to physiological blood flow exhibiting a force on the guidewire that overcomes the frictional force between the guidewire and the CVC lumen, which should prevent guidewire slippage. This is the basis for widely adopted guidance that mandates that operators should hold onto the guidewire at all times while it remains intravascular during CVC insertion. However, this may be an
oversimplification of retention events, as most guidewires are likely to remain intraluminally should the operator inadvertently take their hand off them during the procedure. Indeed, the forces exerted by blood flow and pressure differentials are much greater during arterial
procedures, although in the opposite direction. If these forces were sufficient to overcome friction, guidewires would be ejected from catheters whenever the operator took his/her hand off the guidewire. When retention occurs, the guidewire can migrate from the catheter
into the patient’s vasculature and heart and may cause complications such as arrhythmia, vascular damage, thrombosis, cardiac perforation, and tamponade.”